
Email is one of the most critical and personal forms of communication in the online world. However, email accounts are also vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and identity theft. If your email address or password is compromised, hackers can access your online accounts, steal your personal information, and impersonate you.
Fortunately, some tools can help you monitor your email from breaches and take action if needed. In this blog post, Privacy Hive will introduce two websites that track emails exposed to breaches and provide individuals a way to search if their emails or forwarded emails have been breached: Have I Been Pwned and DeHashed?
Have I Been Pwned
Have I Been Pwned is a website that allows you to check if your email address has been involved in a data breach. It collects and analyzes data from hundreds of sources, including hacked websites, leaked databases, and dark web forums. It also provides information about the type and extent of the breach, such as the date, the number of affected accounts, and the data exposed.
To use Have I Been Pwned, enter your email address in the search box and click on the pwned? button. The website will tell you if your email address has been pwned (i.e., compromised) or not, and if so, in which breaches and what data was exposed.
For example, if we enter the email address bing@outlook.com, we get the following result:
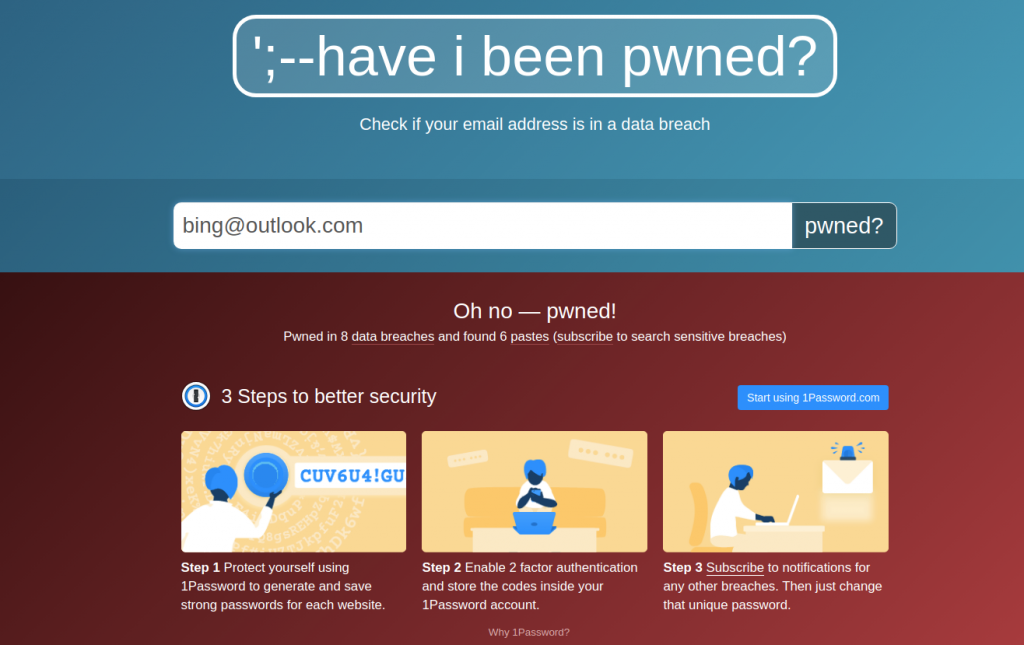
As you can see, the email address has been pwned in 8 data breaches, and the data exposed included name, email address, password, phone number, and physical address.
If your email address has been pwned, you should take some steps to protect yourself, such as:
- Change your password for the affected account and any other account that uses the same or similar password. Use a strong and unique password for each account or a password manager to generate and store them securely.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your accounts, if available. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a code or device and your password to log in.
- Monitor your accounts for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized logins, transactions, or messages. Report any anomalies to the service provider and the relevant authorities.
- Be wary of phishing emails, calls, or texts that claim to be from the breached service or other legitimate entities and ask for your personal or financial information. Please do not click on links or attachments or provide any information unless you know they are authentic.
DeHashed
DeHashed is another website that allows you to search for your email address in leaked databases. It also provides more details about the source and content of the data, such as the file name, size, format, and hash. You can download the data for offline analysis with a paid account.
The website will show you the number of results found and a list of databases that contain your email address. You can click on each database to see more details, such as the data fields, the sample records, and the download link (with a paid account).
Suppose your email address appears in any database. In that case, you should follow the steps mentioned above to have been pwned, such as changing your password, enabling 2FA, monitoring your accounts, and avoiding phishing.
Tips for Choosing a Secure and Private Email Service and Password
While Have I Been Pwned and DeHashed can help you monitor your email for breaches, they cannot prevent them from happening. Therefore, choosing a secure and private email service and password and following some best practices to protect your email privacy and security is essential. Here are some tips to help you do that:
- Choose an email service that offers end-to-end encryption, which means that only you and the intended recipient can read your messages, and no one else, not even the email provider, can access them. Some examples of email services that offer end-to-end encryption are ProtonMail, Tuta, and Mailfence.
- Choose an email service that respects your privacy and does not collect, share, or sell your data or track your online activity. Some examples of email services that respect your privacy are StartMail, Posteo, and Fastmail.
- Choose an email address that does not reveal your personal information, such as your name, location, occupation, or interests. For example, instead of using john.smith@newyork.com, you can use something more generic and random, such as jsm1th1983NY@proton.me.
- Choose a password that is long, complex, and unique and that you can remember. A good password should have at least 12 characters and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. You should also avoid using common words, names, dates, phrases, or any information that can be easily guessed or found online. For example, you can use something like P@ssw0rd!915 instead of a password.
- Use a different password for your online accounts and check them regularly using the previously mentioned services. If one of your accounts is compromised, the hacker cannot access your other accounts with the same password. You can also use a password manager, like Bitwarden, KeePass, or 1Password, to generate, store, and auto fill your passwords securely.
- Be careful when opening, clicking, or downloading anything from your email. Do not open or reply to emails from unknown or suspicious senders that ask for your personal or financial information. Do not click on links or attachments from emails you are not expecting or that look suspicious or too good to be true. Please do not download or run any files or programs from your email unless you trust the source and scan them for viruses or malware first.
Conclusion
Email is a convenient and essential tool for communication, but it also comes with many risks and challenges. Using websites like Have I Been Pwned and DeHashed, you can monitor your email for breaches and stay informed of potential threats. By choosing a secure and private email service and password and following some best practices, you can protect your email privacy and security and prevent hackers from accessing your personal information and online accounts. Remember, your email is connected to everything you do online, so keep it safe and secure. Do not let your email be a hacker’s snack!
